What is DevOps?
- DevOps is simply the unification of the development and operations line-up. DevOps incorporates developer and operation teams to improve collaboration and productivity by automating infrastructure, workflows and continuously measuring application performance.
- DevOps teams try to automate everything. It could be testing a new code or setting up new infrastructure.
- The infrastructure for development includes Planning, Coding, Testing, and Building. In contrast, the infrastructure for operations includes Release, Operate, Deploy, and Monitor.
- In a traditional setup, developers write large chunks of code for their software over weeks or even months. A DevOps mindset allows them to write small pieces of code that are integrated, tested, monitored, and deployed in hours. It will not only increase the frequency of application deployments but also reduce the time required to deploy new code.
- It improves their ability to respond to market demands or other software-related factors.
- Various DevOps tools assist the DevOps team in automating their processes and monitoring application performance.
What are DevOps Metrics?
- DevOps metrics are data sets that directly reveal the performance of a DevOps software development pipeline. And further aids in the rapid identification and removal of bottlenecks. These metrics monitor the application’s technical capabilities and team proceedings.
- DevOps metrics provide a holistic view of the impact and business value of DevOps’s success. By selecting the appropriate performance metrics, one can influence current DevOps initiatives and future production and technological decisions.
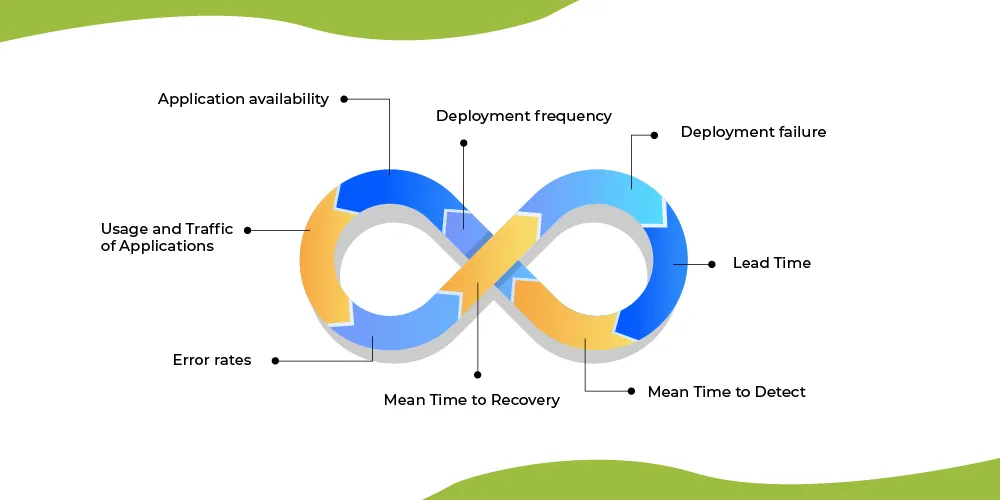
The following are the ten key DevOps metrics that can help businesses monitor the success rate of their apps:
1. Deployment frequency
Track the frequency of code deployment to get a clear picture of how quickly new features and capabilities roll out. This metric should remain stable or increase over time. A decrease or stutter indicates a bottleneck in the DevOps team workflow.
2. Deployment failure
Changes must be implemented smoothly, not just frequently. Maintain the lowest possible failure rate for application changes and releases deployed into production. Potential failures include a change that causes users to time out or entails a rollback for further work. Create a system for monitoring the success and failure of changes. A high rate of change failure impacts the application’s end users. It requires more time spent by administrators troubleshooting issues and fixing bugs rather than completing high-value initiatives.
3. Lead Time
If the goal is to ship code as quickly as possible, this is a critical DevOps metric. Lead time is the actual amount of time that passes between the start of a deliverable and its deployment. It informs you how long it would take to get a new product to manufacture if you start working on it today.
4. Mean Time to Detect (MTTD)
If it takes considerably longer to detect a problem, a low change in failure rate is insufficient. For example, if the mean time to detect is 30 days, it could take almost a month to diagnose the issue that causes failure rates to rise. As DevOps procedures are more established, MTTD ought to decrease with time. Expect the bottlenecks causing these current delays to later bring further congestion to the DevOps workflow if the MTTD increases. For security reasons, rapid detection of the problem proves beneficial as it limits the scope of an attack.
5. Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR)
Mean time to recovery is another important DevOps metric that administrators should keep as low as possible. Remove problems as soon as you become aware of them. DevOps organizations adhere to the principle that frequent, incremental changes are easier to deploy and fix when something goes wrong. When a release contains a high degree of change and complexity, it becomes more difficult to identify and resolve issues. Several factors, including asset type, criticality, and age, influence what constitutes a world-class MTTR. An MTTR of less than five hours, on the other hand, is a good rule of thumb.
6. Application Performance rate
An unexpected surge in end users can cause performance issues at the infrastructure level. Storage bottlenecks, high memory consumption, CPU spikes and network latency are all consequences of increased application usage. Increasing end-user numbers may necessitate the installation of additional infrastructure. Performance drops without other end-user requests. It could also indicate that bugs or inefficient changes from development and release are slowing down the app. To ensure high availability and a positive end-user experience, verify and correct such errors without delay.
7. Usage and Traffic of Applications
Following a deployment, you should check if the number of transactions or users accessing your system appears normal. Something could go wrong if you witness no traffic or a massive spike in traffic. Zero traffic on your application is the last thing you want to see. Alternatively, if you’re using microservices and one of your applications generates a lot more traffic, you might notice a tremendous spike in it.
8. Application availability
Application availability is a metric used to determine whether an application is properly functioning and meets the needs of an individual or business. The availability is determined through application-specific key performance indicators (KPIs), such as overall or timed application uptime and downtime, the number of completed transactions, reliability, responsiveness, and other relevant factors.
9. Error rates
It is crucial to monitor error rates within your application. They indicate not only quality issues but also ongoing performance and uptime issues. Best practices for exception handling are critical for good software. Identify new exceptions in your code following a deployment. That is looking for any signs of bugs. Capture issues with database connections, query timeouts, and other related topics in production.
10. Change failure percentage
The total number of failed deployments is divided by the total number of deployments to yield the change failure percentage metric. Assume your team performs ten deployments per day. There were three return failures out of that total. This scenario has a 30% change failure rate. That is, 30% of the code changes must be fixed or reversed.
Did you know?
- 66% of the organizations surveyed have implemented DevOps for their applications.
- 16% of those organizations saw DevOps as a cost-cutting driver. 49% of the participants credited DevOps for their improved performance, faster market-time, and higher ROI (Return On Investment).
- 48% of respondents said the main reason they weren’t using DevOps was a lack of knowledge, while 33% said they didn’t have the right tools to implement it.
- Version control systems are ranked first on the list of tools that support a DevOps initiative by 84% of those polled. Modern version control systems are the fundamental building blocks of any process involving automation, continuous integration, or delivery.
In a nutshell:
Today’s technology allows you to automate a wide range of tasks. DevOps is the collaboration of software development teams from various departments and locations. DevOps metrics, on the other hand, are a means of measuring the effectiveness of your team’s collaboration and a step toward business advancement.
DevOps Tools That Aid In Your Organization